Medical Consultation and Treatment for Overseas Patients
About QST hospital
Carbon ion radiotherapy is characteristically suited for the treatment of cancer (Refer to characteristics of carbon ion radiotherapy). The QST hospital has been a world-leader in its application since 1994 and also accepts patients from overseas. When patients hope to contact us regarding indication of carbon ion radiotherapy, they should contact us through a registered guarantor (medical coordinator or travel agency). For coordinator details, please send an e-mail to the following address.
kokusaiml@qst.go.jp
Please state your name and country of residence in the e-mail.
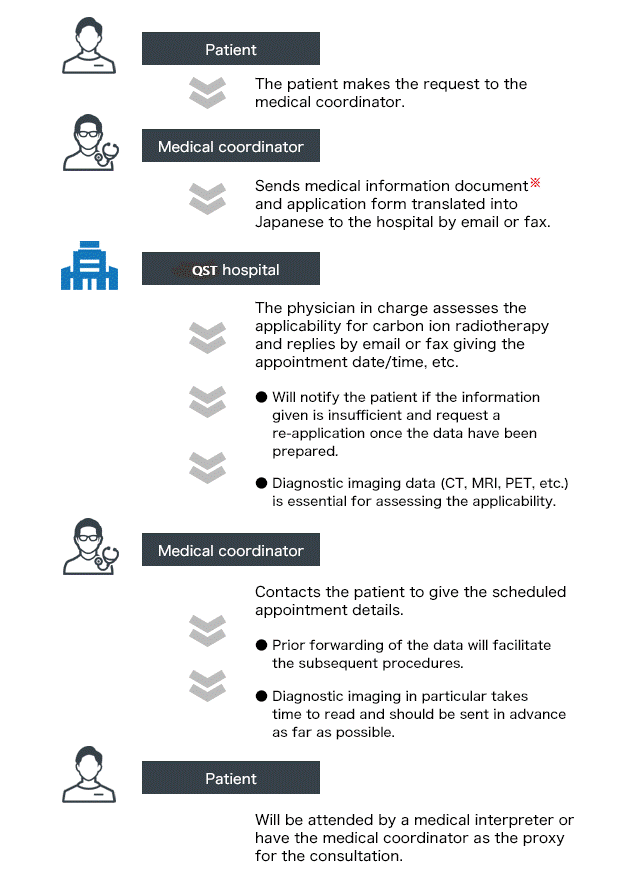
Process of receiving consultations/treatment
Applicable disorders
- Lesions specified by the Japanese Society for Radiation Oncology “proton beam therapy guidelines by disease”:
- Cranial base, head and neck, lung, liver, pancreas, prostate, bone and soft tissue, uterus, lymph node/※lung/liver metastases, etc. (Refer to applicable disorder websites).
- Other lesions of which treatment can be of some benefit to the patient in terms of the survival rate, local control and quality of life (QOL), etc. For example, the therapy may be applied even in cases of recurrence following radiation therapy or synchronous multiple cancers.
- The QST physician in charge shall give the final assessment of the applicability for treatment in the above cases after viewing the data. ※The patients from overseas with breast cancer and esophageal cancer are not accepted.Please contact us for details
Treatment period of main disorders in the QST hospital
| Disorders | Treatment period |
|---|---|
| Head and neck cancers | 4 weeks |
| Lung cancer | Stage I cancer 1 day to 3 weeks, locally advanced cancer 4 weeks |
| Liver cancer | 2 days to 3 weeks |
| Pancreatic cancer | 3 weeks |
| Prostate cancer | 3 weeks |
| Bone and soft tissue tumors | 4 weeks |
| Colorectal cancer (post-operative recurrence) | 4 weeks |
| Uterine cancer | 5 weeks |
Essential information for the assessment of applicable disorders or for the initial consultation
Please contact us by email.
Process from initial consultation to treatment
The treatment preliminaries shall commence soon after carbon ion radiotherapy is assessed as applicable. Please check here for the process following the initial consultation to treatment.
Process of carbon ion radiotherapy
Once the treatment preliminaries have been completed, you will have free time of approximately 1~2 weeks until the treatment commences. If you plan to a visit back home, you should return by the day prior to commencement of the treatment. Since the treatment period is subject to change, please consult the physician on the date of your return home including the schedule for tests and examinations.
Treatment costs
The QST hospital has set the following for the medical costs, etc. of overseas patients who do not subscribe to Japan’s public health insurance.
- Costs of carbon ion radiotherapy → private patient payment 5.786 million yen (tax included).
- In addition, medical costs for hospitalization, follow-up consultations and tests, etc. shall be calculated at a rate of 33 yen per medical fee point (tax included).
※The service fee for medical coordinators is not included.
Advantages of carbon ion radiotherapy
- Can deliver radiation to lesions with pinpoint accuracy (and with minimal side effects)
- Is highly bioactive (also effective for cancers resistant to radiation therapy)
- Requires a short treatment time (can reduce the period of stay)
- Is also user-friendly for elderly persons and does not hurt
The following is slightly technical, but the above advantages are due to the physical and biological characteristics of Carbon ions.
Characteristics of carbon ion radiotherapy
Since carbon ion radiotherapy uses carbon particles which are 12 times heavier than protons, it possesses properties that make it suitable for the treatment of cancer due to its improved physical dose distribution and biological effects.
- The in vivo formation of high-dose areas (referred to as “Bragg peaks”) makes irradiation targeting the cancer lesion easier than with conventional X-rays and also minimizes adverse effects on the surrounding healthy tissue.
- The biological (cell killing) effect of the peak area is 2 to 3 times greater than X-rays or proton beams and the treatment is therefore also effective for cancers showing resistance to conventional X-rays.
- The properties referred to in 1 and 2 above are manifested in a form suitable for the treatment of cancer. In short, the biological (cell killing) effect of carbon ions is characterized by being minimal when close to the surface of the body but increasing with penetration to a maximum in the peak area. Accordingly, aligning the carbon ion peak area with the location and size of the lesion means that both physically and biologically a greater dosage (impact) can be given to the lesion instead of to the surrounding healthy tissue.
Contact for enquiries to the QST hospital:
- QST Hospital International Cooperative Division
- 4-9-1 Anagawa, Inage-ku, Chiba-shi, Chiba 263-8555
- Email:kokusaiml@qst.go.jp
- TEL:+81-43-206-3181
 OPEN
OPEN